Every cyclist knows the thrill of a smooth ride. But few understand the hidden heroes behind it: how many bearing on each side of a bycycle hub. As someone who’s spent countless miles exploring, I’ve learned that these tiny marvels are key to your bike’s performance.
Your bicycle hub bearings are more than just metal parts. They’re precision-engineered systems that make your wheels spin smoothly. They help you glide across different terrains and make your ride more enjoyable. Knowing about hub anatomy and bearing configuration is important for every rider.
Whether you’re a weekend warrior or a serious cyclist, knowing about your bike’s hub bearings can improve your ride. This guide will explore the world of bicycle hub bearings. It will show their crucial role in your cycling adventures.
Key Takeaways
- Hub bearings are critical for smooth wheel rotation
- Proper bearing configuration impacts riding performance
- Different bikes require different bearing setups
- Regular maintenance extends bearing lifespan
- Understanding hub anatomy helps cyclists make informed decisions
Introduction to Bicycle Hub Bearings and Their Importance
Your bike’s performance is key to a great ride. At the center of this is the hub bearing system. It’s small but crucial for a smooth ride.
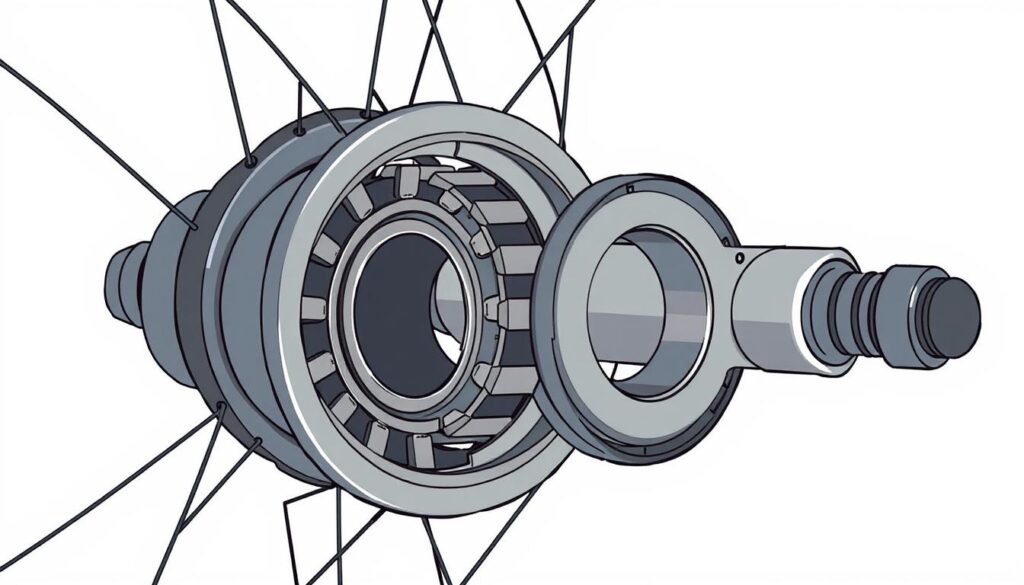
Learning about bearings can change your cycling. They help your wheels spin smoothly, making your ride better.
Why Proper Bearing Setup Matters
A good hub bearing system brings many benefits:
- Less mechanical resistance
- Smooother wheel rotation
- Longer wheel and bike life
- Better cycling efficiency
“The difference between a good and great ride often comes down to the smallest mechanical details.” – Professional Cycling Technician
Basic Hub Anatomy Overview
The hub has important parts working together. You’ll find inner races, ball bearings, and an outer race. Each part helps the wheel spin smoothly and evenly.
Impact on Riding Performance
Getting your bearings right is key to a good ride. Worn or bad bearings can slow you down and make pedaling harder. Keeping them in good shape is essential.
By taking care of your bearings, you’ll enjoy a better and more efficient ride.
How Many Bearings on Each Side of a Bicycle Hub
Knowing how many bearings are on each side of a bicycle hub is key for better riding. Most hubs have between two to four bearings per side. This depends on the bike type and how you plan to use it.

- Bicycle type (road, mountain, touring)
- Intended riding conditions
- Hub design and manufacturer specifications
Here’s what you can usually find in standard bicycle hubs:
- Road bike hubs: Typically 2 bearings per side
- Mountain bike hubs: Often 3-4 bearings per side for increased durability
- High-performance hubs: May feature specialized bearing arrangements
The number of bearings affects how smoothly your bike moves. It also reduces friction and boosts your ride’s efficiency. Having the right number of bearings helps spread out weight and handle rotational forces.
Pro cyclists know that the right bearing configuration can make a significant difference in performance and longevity.
It’s wise to check your hub’s bearing count during regular maintenance. Each side of the hub is vital for your bike’s smooth motion and control.
Types of Bearings Used in Modern Bicycle Hubs
The performance of a bicycle hub greatly depends on the bearings it uses. Knowing about the different bearing technologies helps you choose the right parts and take care of your bike.

Today’s bicycle hubs come with various bearing technologies. Each type has its own features that affect how well your bike rides and lasts.
Ball Bearings vs. Cartridge Bearings
Bicycle hubs mainly use two kinds of bearings:
- Ball bearings: These are the old-school type that need to be put together by hand and need regular checks
- Cartridge bearings: These are pre-assembled and easier to swap out. They also keep out dirt and water better
Sealed vs. Open Bearing Systems
Choosing between sealed and open bearings affects how well your bike performs over time:
- Sealed bearings keep out dirt and water
- Open bearings are easier to clean but need more upkeep
Material Differences in Bearing Construction
The materials used in bearings play a big role in how well they work and how long they last. Steel, ceramic, and hybrid materials each have their own benefits for different types of riding.
Choosing the right bearing type can make your bike roll smoother and save you money on maintenance in the long run.
Front Hub Bearing Configuration and Assembly

Knowing about front hub bearings is key for a smooth bike ride. The front hub assembly is vital for a smooth ride. The bearing setup affects how well your wheel spins and handles different terrains.
Front hub bearings are made with care for the best wheel movement. Most bikes have two bearings on each side of the hub. This setup helps the wheel spin smoothly and stably.
- Standard front hub bearing count: 2 bearings per side
- Bearing types: Ball bearings or cartridge bearings
- Primary materials: Steel, ceramic, or hybrid compositions
When putting together front hub bearings, there are important steps:
- Aligning bearing races correctly
- Applying the right lubrication
- Adjusting tension accurately
- Ensuring smooth wheel rotation
| Bearing Type | Durability | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearings | Good | Standard |
| Cartridge Bearings | Excellent | High |
| Sealed Bearings | Very Good | Premium |
Experts say to check your front hub bearings often. Regular care can make your hub last longer and ride better in all conditions.
Rear Hub Bearing Layout and Design Features
For cyclists, knowing about rear hub bearings is key. They are different from front hub bearings because of the unique demands of riding. This knowledge helps improve performance and durability.
Rear hub bearings are set up to handle different stresses on each side. The design of these bearings greatly affects your bike’s performance and how smoothly it runs.
Drive Side Bearing Specifications
Drive side bearings face more stress and load. They are built with:
- Larger bearing diameter
- More robust construction
- Enhanced load-bearing capacity
- Precision-engineered seals
Non-Drive Side Bearing Requirements
Non-drive side bearings are key for keeping the wheel straight and reducing side movement. Their design includes:
- Precise alignment mechanisms
- Lighter weight construction
- Reduced friction characteristics
- Smooth rotational performance
Special Considerations for Cassette Hubs
Cassette hubs have their own design challenges. They need balanced bearing setups to work well with the freehub mechanism and ensure smooth power transfer.
Cyclists should really focus on their rear hub bearings. They are crucial for the bike’s performance and the overall riding experience.
Bearing Size Standards and Compatibility
Knowing about bearing size standards is key for your bike’s hub to work well. Different makers use certain sizes that affect your bike’s ride. When picking new bearings, look closely at the measurements and make sure they fit right.
Bicycle hub bearings come in many standard sizes. Knowing the right size can save you time and money. Here are important things to think about when matching bearing size standards:
- Outer diameter of the bearing
- Inner diameter of the hub axle
- Bearing width and thickness
- Material composition
Bearing compatibility is more than just size. You also need to think about the type of bearing system your hub uses. Some bikes have sealed cartridge bearings, while others use loose ball bearings. Each type has its own size needs that affect the hub’s dimensions.
| Bearing Type | Typical Diameter Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Cartridge | 15-24mm | Modern road and mountain bikes |
| Loose Ball | 10-20mm | Older or specialty bicycle models |
Pro tip: Always measure your current bearings carefully before buying new ones. A digital caliper can give you accurate measurements. This ensures the new bearings will fit perfectly with your hub’s design.
Common Hub Bearing Problems and Solutions
Bicycle hub bearings are key to a smooth ride. Knowing when they wear out helps keep your bike running well and saves money on repairs.
Spotting early signs of bearing damage is vital for keeping your bike in top shape. A well-maintained bike rides smoothly thanks to its bearings.
Signs of Bearing Wear and Damage
- Grinding or gritty feeling when spinning the wheel
- Noticeable side-to-side wheel movement
- Decreased wheel smoothness
- Visible rust or corrosion on bearings
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular care for your bearings can make them last longer. Here are some tips to help:
- Clean hub bearings after wet or muddy rides
- Apply appropriate bicycle-specific grease
- Check bearing tension periodically
- Store bicycle in dry conditions
When to Replace Hub Bearings
Knowing when to replace bearings can prevent problems on the road. Replace them when:
| Condition | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Excessive play in wheel | Immediate replacement recommended |
| Rough rotation | Inspect and likely replace |
| Visible bearing damage | Replace entire bearing set |
Replacing bearings before they fail can prevent bigger problems. Always get a pro’s opinion if you’re not sure about your bearings.
Upgrading Your Hub Bearings for Better Performance
Bicycle lovers can make their rides better by upgrading their hub bearings. These upgrades are key for smoother, more efficient rides and less friction.
When looking to upgrade your hub bearings, consider a few important things:
- Riding style and intensity
- Budget constraints
- Maintenance requirements
- Desired performance improvements
Ceramic bearings are a top choice for serious cyclists. They offer big benefits:
- Less friction
- Lighter weight
- Longer durability
- Better heat resistance
| Bearing Type | Performance Rating | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Steel Bearings | Good | $20-$50 |
| Ceramic Hybrid Bearings | Excellent | $100-$250 |
| Full Ceramic Bearings | Premium | $250-$500 |
Your cycling needs will guide you to the right hub bearing upgrades. Professional cyclists often choose ceramic bearings for racing. But, casual riders might find standard steel bearings more affordable.
Pro tip: Always talk to a bike expert to find the best bearing upgrades for you.
Conclusion
Understanding bicycle hub bearings is key to keeping your bike in top shape. This guide has covered the basics of hub bearings, from front to rear wheels. Knowing about them can greatly improve your cycling experience.
Keeping your bike’s bearings well-maintained is essential. Spotting wear signs and knowing the different types of bearings helps prevent big problems. Regular checks and timely replacements keep your bike running smoothly.
Every bike is different, and so are its hub bearing needs. Whether you ride for fun or competitively, caring for your bearings is worth it. It leads to a better ride, less friction, and a longer-lasting bike.
Now you’re better equipped to handle bike maintenance. Make it a habit to check your bearings often. Learn about their unique features and ask for help when needed. A well-kept bike is always ready for your next adventure.

1 thought on “How Many Bearings Are on Each Side of a Bicycle Hub? – Avoid Costly Mistakes with This Essential Info”